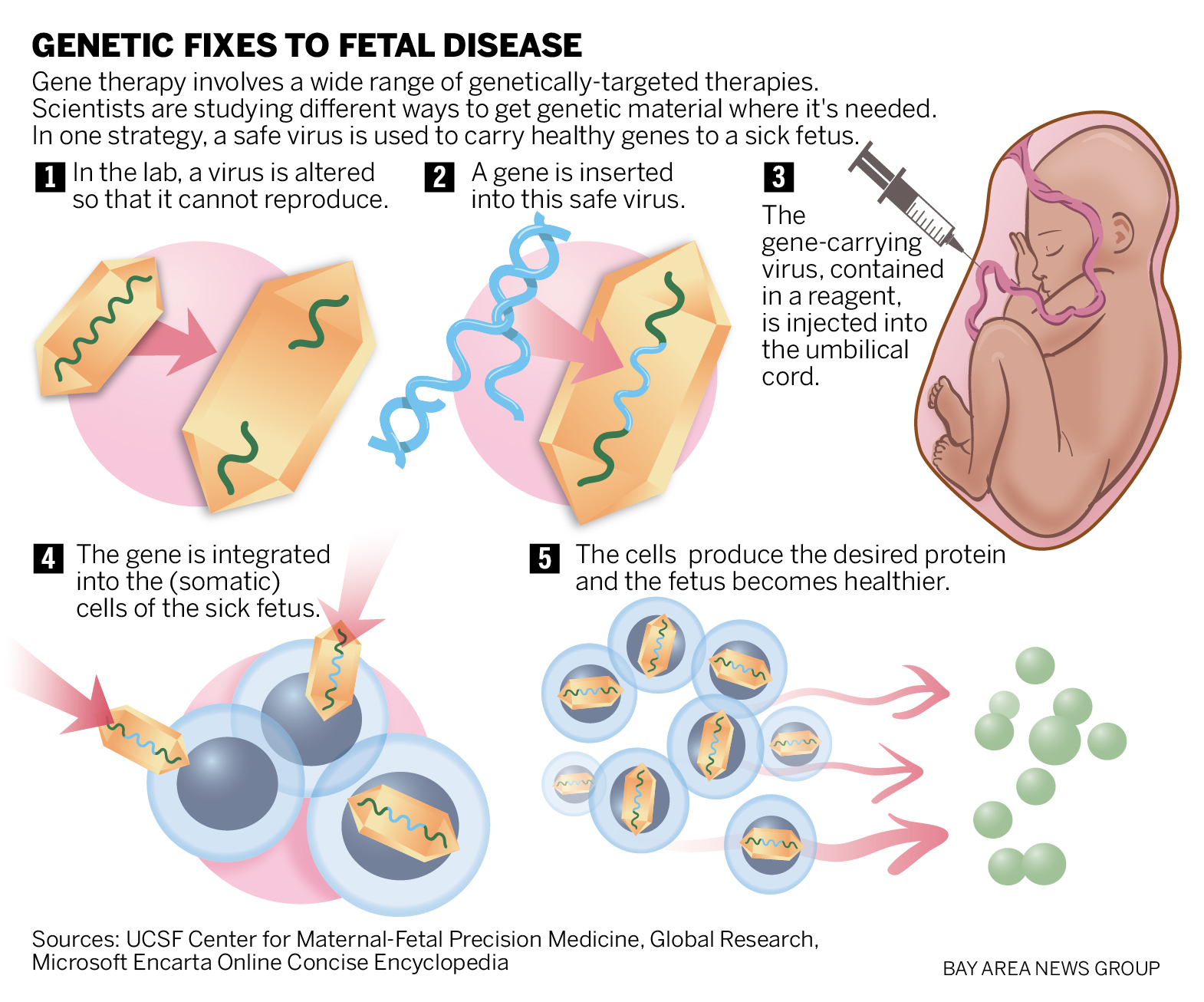
Fetal genetic disorders pose significant challenges during pregnancy, but advancements in prenatal genetic testing are changing the landscape of maternal-fetal medicine. These disorders encompass a range of genetic conditions that, if detected early, may be manageably treated before or shortly after birth. With nearly 300 treatable genetic conditions identified through recent studies, the potential for early intervention in genetics is becoming increasingly viable. Techniques like genomic sequencing pregnancy can now identify genetic disorders, offering families valuable options to increase health outcomes. Timely detection of genetic disorders in pregnancy not only enhances prenatal care but also empowers parents with knowledge and actionable steps to take for their unborn child.
Understanding fetal genetic abnormalities is crucial for expecting parents, as these conditions can greatly impact a child’s health and future. Often termed congenital genetic disorders, these issues arise from various genetic factors and may require intervention as early as gestation. Emerging approaches in early diagnosis, such as cutting-edge genomic analysis, allow healthcare providers to assess and manage these conditions proactively. With the rise of genomic sequencing and a deeper comprehension of treatable genetic anomalies, families are now afforded the opportunity to make informed decisions during pregnancy. The integration of genetic counseling and innovative testing methods is vital to navigating the complexities presented by these potentially life-altering disorders.
Understanding Fetal Genetic Disorders
Fetal genetic disorders refer to a variety of conditions that arise from anomalies in the fetus’s genetic makeup. These disorders can range from single-gene mutations to chromosomal abnormalities. Identifying these issues during pregnancy is crucial, as early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and management that can significantly improve outcomes. Technologies like genomic sequencing pregnancy allow for the detection of these disorders at an early stage, often before the fetus is even born. This means that parents can be equipped with knowledge and a plan of action to address potential health issues.
The growing list of treatable fetal genetic disorders expands the possibilities for personalized prenatal care. By proactively diagnosing conditions that can be managed prior to birth, healthcare providers aim to reduce the risks of severe complications that could arise after delivery. For instance, disorders that previously led to serious health consequences can now be addressed in utero, offering families a new perspective on the management of genetic disorders during pregnancy.
The Role of Prenatal Genetic Testing
Prenatal genetic testing has revolutionized the way we approach fetal health, providing critical insights into potential genetic disorders pregnancy can bring. These tests include techniques such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS), amniocentesis, and non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT). Each of these methods has its own set of benefits and limitations but collectively they contribute to a comprehensive understanding of a fetus’s health. By integrating prenatal genetic testing into regular pregnancy care, families can better prepare for any medical interventions that may be needed.
Moreover, early identification through prenatal genetic testing not only fosters informed decision-making for parents but also enhances the roles of medical professionals. It creates an opportunity for geneticists and obstetricians to work closely together in developing tailored care plans. This collaborative approach ensures that if a prenatal diagnosis reveals a treatable genetic condition, necessary interventions can be initiated promptly, minimizing risks and paving the way for improved long-term health outcomes.
Emerging Treatments for Genetic Conditions During Pregnancy
Recent advancements in medical science have enabled the development of therapeutic strategies aimed at treating genetic conditions before birth. This move towards early intervention highlights the importance of understanding and identifying genetic disorders as early as possible, allowing healthcare providers to implement treatment plans that can alter the progression of these diseases. By leveraging genomic sequencing and an ever-growing body of knowledge on treatable conditions, clinicians can make informed decisions that prioritize the health of both the fetus and the mother.
The implications of these emerging treatments extend beyond immediate health effects. They offer hope to families who might otherwise face devastating diagnoses. Treatments that can be administered in utero, such as gene therapy or medication addressing specific fetal conditions, have the potential not only to prevent complications but also to fundamentally change the narrative for families experiencing genetic disorders. This capability represents a significant shift from traditional approaches, underscoring the transformative impact of early intervention genetics.
Benefits of Early Intervention Genetics
The practice of early intervention genetics aims to address genetic disorders proactively, rather than reactively. By identifying fetal genetic disorders through advanced testing techniques, healthcare providers can develop not only treatment plans but also supportive resources for families. These early interventions can lead to better health outcomes for newborns and offer parents peace of mind knowing they are taking active steps to manage potential health risks from the beginning.
Additionally, by effectively communicating potential interventions and treatment options available, genetic counselors and healthcare teams can empower families. Providing parents with education about treatable conditions ensures they feel supported throughout their pregnancy journey. With the ability to intervene early, many genetic disorders that could otherwise lead to lifelong disability or health complications can be managed effectively, acknowledging that knowledge and timely action are vital.
Challenges in Managing Genetic Disorders During Pregnancy
Despite the promising advancements in identifying and treating fetal genetic disorders, there are notable challenges that healthcare professionals and families face. The ethical implications of genetic testing can be complicated, requiring thoughtful consideration and clarity from both geneticists and obstetricians. For many parents, the prospect of receiving extensive information about possible genetic disorders can be overwhelming, leading to anxiety and uncertainty during what should ideally be a joyful time.
Moreover, the integration of new genetic information into prenatal care necessitates significant collaboration between medical specialists. Genetic counselors, obstetricians, and pediatricians must work cohesively to create an environment where expectant parents feel informed and supported. This collective effort is crucial for navigating the complexities of genetic disorders and ensuring that parents receive comprehensive care options that align with their desires and needs.
The Importance of Collaboration in Prenatal Care
Collaboration among healthcare professionals is pivotal in enhancing the management of fetal genetic disorders. Medical geneticists, obstetricians, and ethicists must unite their expertise to ensure that patients receive clear and actionable information regarding genetic testing and treatment options. Such teamwork not only allows for a holistic approach to prenatal care but also fosters an environment where expectant parents are encouraged to ask questions and explore their options confidently.
Ultimately, a coordinated approach facilitates better decision-making for families planning their next steps upon receiving prenatal test results. By establishing a strong support network that includes a range of specialists, healthcare teams can empower expectant parents, giving them access to the information they need to feel equipped in addressing any genetic disorders that may present during pregnancy.
Future Perspectives on Genetic Research in Prenatal Care
As genetic research continues to evolve, the future of prenatal care holds immense promise for addressing fetal genetic disorders. Investigations into the underlying genetics of various disorders are crucial for developing effective treatments and interventions that can be applied during pregnancy. With advances in technology and understanding of genomics, researchers are uncovering new ways to approach genetic conditions that were previously deemed untreatable.
Additionally, as new therapies emerge, ongoing education for healthcare professionals will be essential in adapting practices to incorporate the latest developments in fetal genetics. By staying informed about the potential for treating genetic disorders during pregnancy, obstetricians and geneticists can continuously provide the most effective and up-to-date care for their patients. This commitment not only enhances the patient experience but also builds a foundation for a more hopeful outlook on the genetic challenges faced by families.
The Role of Genetic Counseling in Preparing Families
Genetic counseling plays a critical role in guiding families through the complexities of fetal genetic disorders. Counselors provide expert insights and personalized information based on the specific genetic backgrounds of the parents. This guidance is essential for understanding the risks associated with genetic conditions and making informed choices about prenatal testing and management options. By addressing concerns and questions early in the pregnancy, genetic counselors help mitigate anxiety and empower families to take proactive steps.
Furthermore, genetic counseling serves as a bridge between the medical team and the family, ensuring that parents comprehend the implications of their genetic testing results. With the support of a knowledgeable counselor, families can navigate the available interventions for treatable fetal conditions, fostering a better understanding of how to manage potential health issues right from the start of their child’s life.
Navigating New Health Information During and After Pregnancy
Navigating new health information related to fetal genetic disorders can be an overwhelming task for many families. The bombardment of medical terms, potential treatment options, and implications of genetic findings may create confusion for expectant parents. It is essential for healthcare teams to present this information in a clear, concise manner that minimizes emotional stress while maximizing understanding of available options.
Postnatal, the landscape can remain complex as families adapt to new health regimens or prepare for ongoing therapies. Empowering families with knowledge and access to resources is vital in ensuring they feel equipped to manage any genetic conditions their child may face. Through continued support and communication from healthcare professionals, families can more confidently navigate this new chapter while focusing on their child’s well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are fetal genetic disorders and how are they identified?
Fetal genetic disorders refer to genetic conditions that can affect a developing fetus during pregnancy. These disorders can be identified through prenatal genetic testing, which includes methods like genomic sequencing to detect specific genetic anomalies or conditions that may require early intervention.
How can prenatal genetic testing help in the management of fetal genetic disorders?
Prenatal genetic testing allows for the early identification of fetal genetic disorders, enabling healthcare providers to offer potential treatment options during pregnancy or shortly after birth. This proactive approach can improve outcomes by facilitating early intervention genetics for actionable conditions.
What are some examples of treatable genetic conditions identified during pregnancy?
Recent research has identified nearly 300 treatable genetic conditions, ranging from congenital heart defects that can be managed with medication to gastrointestinal disorders that require fluid and electrolyte therapy. These conditions can significantly benefit from early intervention before or shortly after birth.
What role does genomic sequencing pregnancy play in detecting genetic disorders?
Genomic sequencing during pregnancy plays a crucial role in identifying genetic disorders by analyzing the fetus’s DNA. This technology helps uncover genetic anomalies that may not be visible through traditional imaging methods, aiding in timely and accurate diagnosis.
How might early intervention affect the outcomes of fetal genetic disorders?
Early intervention for fetal genetic disorders can significantly alter the prognosis for the affected child, potentially reducing morbidity and improving long-term health outcomes. Interventions may include medical treatments or therapies initiated before birth or within the first days of life.
What challenges do families face when learning about fetal genetic disorders?
Families may feel overwhelmed by the amount of information regarding fetal genetic disorders and the options available for prenatal care and treatment. It is essential for healthcare providers to communicate effectively, ensuring that families understand the implications and choices associated with diagnosis and potential interventions.
Why is collaboration among medical professionals important for fetal genetic disorders?
Collaboration among medical geneticists, obstetricians, and ethicists is vital to navigate the complexities of diagnosing and managing fetal genetic disorders. A unified care team can provide families with clear, comprehensive information, ensuring informed decision-making and enhancing patient care throughout the pregnancy.
What is the significance of the treatable fetal findings list?
The treatable fetal findings list is significant because it aggregates genetic disorders that can be acted upon during pregnancy or shortly after birth. This list empowers healthcare providers to offer targeted interventions that can improve health outcomes for fetuses diagnosed with genetic conditions.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Purpose | To identify genetic disorders that can be treated during pregnancy or shortly after birth. |
| Number of Disorders Identified | 296 genetic conditions categorized as treatable. |
| Importance of Detection | Timely detection can reduce morbidity, offering opportunities for early intervention. |
| Role of Genomic Sequencing | Genomic sequencing is crucial for prenatal diagnosis and identifying disease-related genes. |
| Authors and Institutions | The study was conducted by researchers from Harvard Medical School, Mass General Brigham, and Duke University School of Medicine. |
| Ethical Challenges | There are ethical considerations and potential for information overload for patients. |
| Potential Benefits | Early intervention can alter disease progression and improve patient outcomes. |
Summary
Fetal genetic disorders can significantly impact the health of a fetus and newborn; however, advancements in research have highlighted various genetic conditions that may be treated prior to birth. A recent study has identified 296 fetal conditions that can potentially be managed through timely intervention, showcasing the importance of early genetic screening during pregnancy. The potential to minimize morbidity and improve outcomes underscores the necessity of integrating fetal genetic testing into prenatal care, enabling families to make informed decisions and pursue beneficial treatments for their children.